Exploring Affordable Phones and Unlimited Data
This guide discusses the intriguing benefits of acquiring affordable phones equipped with unlimited data plans through government-supported programs. These initiatives aim to connect individuals by providing essential communication tools to qualifying low-income households. Understanding this framework is vital for those seeking to access telecommunications services without financial burdens.

An Introduction to Government-Supported Phone Programs
In today's digital era, having access to reliable communication devices is essential for both personal and professional purposes. The concept of receiving affordable phones with unlimited data is not just a dream; it’s a reality for many individuals who find themselves at a financial disadvantage. Several government-supported programs aim to alleviate the burden of phone accessibility, providing necessary technologies to help bridge the digital divide and support those in need. Here, we delve into these initiatives, explain how they work, who qualifies, and how you can apply.
Understanding the Basics of Affordable Phones and Unlimited Data
Affordable phone programs offering unlimited data are primarily designed to target low-income families, ensuring they can remain connected regardless of their financial situation. This is crucial as digital communication is increasingly necessary for everyday tasks such as applying for jobs, managing health services, and connecting with loved ones. These programs are part of the broader Lifeline Assistance program and the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP), both of which are backed by federal guidelines and designed to provide essential resources to vulnerable populations.
The Lifeline program was first established in 1985, aimed at ensuring that low-income consumers could still stay connected to vital communication networks. Over the years, this program has expanded significantly to include not only phone services but also internet connectivity, recognizing the evolving landscape of digital communication. Similarly, the Affordable Connectivity Program was introduced more recently to enhance these efforts, providing subsidies specifically for internet access in addition to phone services.
How Do These Programs Operate?
The core aim of these affordable phone programs is to offer eligible applicants either a complimentary smartphone or the option to use their existing devices, accompanied by data, text, and voice services. This makes it possible for individuals to engage in necessary communication without facing financial hardships. Key providers in this sector include SafeLink Wireless, Assurance Wireless, StandUp Wireless, Access Wireless, and True Wireless. Each of these providers has unique offerings but operates under similar federal guidelines to maintain service standards and ensure a consistent level of quality in service delivery.
When applying for these services, consumers can generally expect to receive essential features such as unlimited texting and calling, along with a set amount of data. The specifics can vary, but most of these services are structured to provide sufficient communication capabilities for everyday needs. The affordability aspect is particularly crucial in today’s marketplace where telecommunication options can be prohibitively expensive for those with limited means.
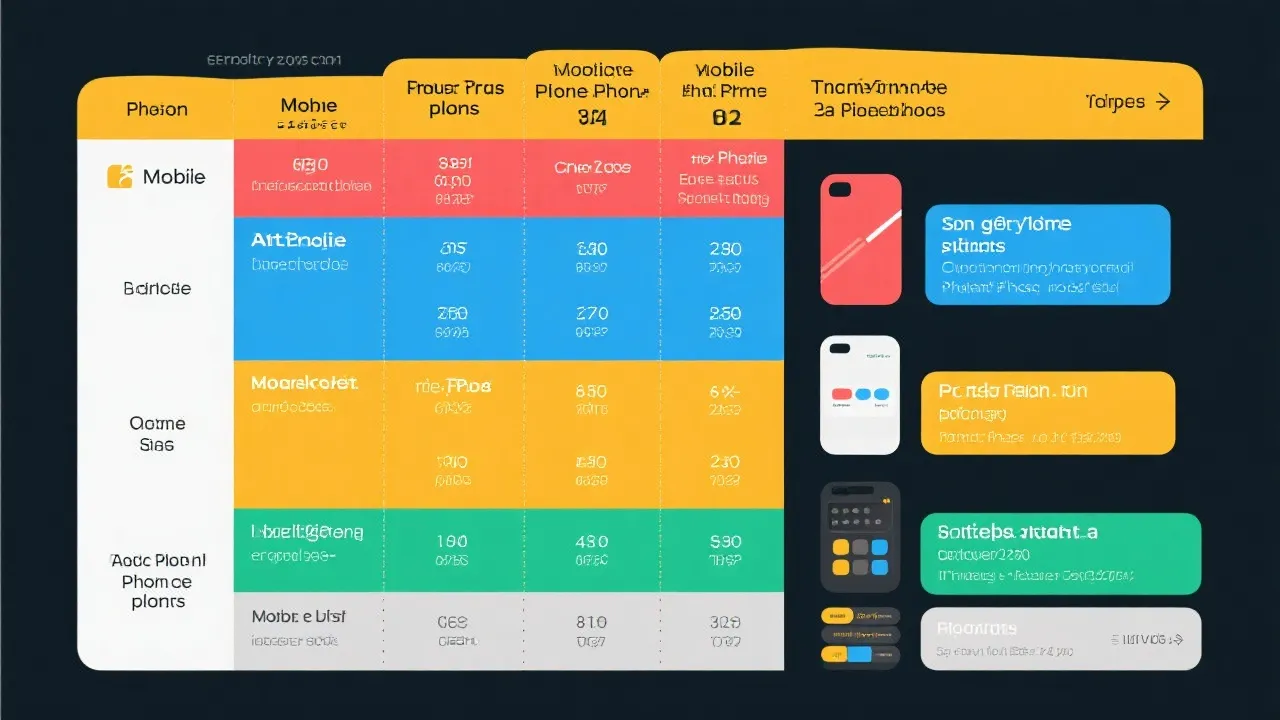
Provider Comparison and Services
| Provider | Main Services | Additional Costs |
|---|---|---|
| SafeLink Wireless | Affordable smartphone or BYOD, unlimited text, calls, data | Premium upgrades, extra data costs |
| Assurance Wireless | Affordable Android phone, unlimited talk, text, data allowance | High-speed data, international calls |
| StandUp Wireless | Affordable smartphone or BYOD, unlimited talk, text, data | Phone upgrades, extra data fees |
| Access Wireless | Unlimited voice, text, limited high-speed data | Data boosts, device upgrades |
| True Wireless | Affordable phone with government support, voice and data plans | Device upgrades, extra data plans |
As illustrated in the table, each provider has its unique set of services and potential additional costs. Understanding these differences is essential for applicants when deciding which provider best meets their needs. For example, while SafeLink Wireless may not charge for basic text, call, and data services, users might face premium charges if they desire a higher-end device or need extra data. Similarly, Assurance Wireless offers only limited high-speed data, which may not be sufficient for users who rely heavily on internet services.
How to Apply and Eligibility Requirements
Applicants must meet specific criteria to qualify for these services, which typically include:
- Income at or below 135% of the federal poverty guidelines for Lifeline; 200% for ACP.
- Participation in government assistance programs like Medicaid, SNAP, SSI, or FPHA.
- Residents on Tribal lands may receive additional benefits.
To assist users in understanding the eligibility requirements better, let’s explore some of the qualifying programs:
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) provides monthly benefits to low-income households, allowing them to purchase the food they need. Those who qualify for SNAP are usually eligible for government-supported phone programs. Likewise, individuals enrolled in Medicaid (the medical care program for low-income individuals) also stand to be eligible, as their participation indicates a financial need.
Furthermore, Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is another important assistance program that supports those who are aged, blind, or disabled and have little or no income. Qualification for SSI can thus serve as a gateway to receiving an affordable phone. The Federal Public Housing Assistance (FPHA) program, which assists low-income families in securing affordable housing, can also make residents eligible for these programs. Finally, those living on Tribal lands often have access to enhanced benefits, recognizing the historical and systemic challenges faced by Native American populations.
The application process itself involves completing an online form, submitting proof of eligibility, and perhaps undergoing a verification process via phone. Each provider lists the detailed requirements and process on their respective websites. Typically, the procedure is straightforward: if the qualifying criteria are met, approval is expected. It is advisable to gather all required documentation before initiating the application to streamline the process and avoid unnecessary delays.
Sources and References
The data provided here is based on publicly accessible resources as of October 2023. Interested individuals can visit the following websites to explore specific offerings and the latest updates:
FAQs
Who qualifies for an affordable phone?
Eligibility is determined by income levels or participation in federal assistance programs like SNAP or Medicaid. It is beneficial for individuals to review the specific poverty guidelines and program requirements, as these can change annually.
Can I keep my current phone number?
Many providers allow users to retain their current phone numbers when switching services, a process known as "porting" a number. This helps users maintain continuity and keeps important contacts accessible. It is critical, however, to check with the specific provider as policies may vary.
Is there a fee for applying?
Applying for an affordable phone program is generally free of charge. However, users should be aware that while the application itself may not carry any fees, additional services such as high-speed data plans or device upgrades could incur extra costs. Always review the terms and conditions outlined by your chosen provider.
Potential Impact of Government-Supported Phone Programs
Government-supported phone programs have a profound impact on individuals and communities, especially in a world that increasingly relies on technology for everyday interactions and activities. The benefits of these programs go far beyond mere access to a mobile phone; they play a crucial role in enhancing quality of life, fostering economic mobility, and promoting social inclusion.
For instance, having access to a smartphone can significantly improve job prospects for low-income individuals. Job hunting often requires the ability to communicate quickly and effectively with potential employers, submit applications online, and receive critical notifications about interviews. Individuals without reliable access to such technology can find themselves at a distinct disadvantage in an already competitive job market.
Moreover, the ability to stay connected isn’t just about employment; it also relates to accessing healthcare services. Telemedicine has become a vital resource, allowing patients to consult healthcare providers without the need to visit offices physically, saving both time and money. Those without adequate communication tools may struggle to access essential healthcare resources, exacerbating already existing health disparities.
Adding to that, education is another area where these programs can make a significant difference. As schools and educational institutions have increasingly turned to online platforms for both learning and communication, students from low-income families may find themselves unable to participate in educational activities due to lack of internet access or smartphones. Government-supported phone programs help to alleviate this issue, ensuring children have the necessary tools to learn effectively and engage with their peers and teachers.
Advocacy and Future of Government-Supported Phone Programs
The evolution of government-supported phone programs reflects a growing recognition of the necessity of connectivity in modern society. Advocacy for affordable communication options continues to gain momentum as more voices raise concerns about the digital divide, which places an increasing number of individuals and families at risk of being left behind in our technology-driven world.
Stakeholders, including community organizations, policy makers, and citizens, are working collaboratively to bring awareness to these issues. Proposals to increase federal funding for Lifeline and ACP initiatives often emerge in response to changing social dynamics, particularly highlighting the need for greater access among underserved communities. Additionally, as technology advances and service requirements grow, there may be discussions around enhancing the service offerings within these programs. This could include provisions for 5G data access or advanced smartphones that can better support educational apps, telehealth services, and other critical applications.
Moreover, as our world becomes increasingly interconnected, the argument for universal access to communication tools becomes more compelling. The notion of connectivity as a fundamental right is taking hold in discussions concerning social justice, economic equity, and community development. Ensuring that everyone has the means to participate in and contribute to society—through digital platforms and services—is becoming a unifying goal among diverse advocacy groups, ultimately driving policy change and enhancing support structures within these government programs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, government-supported phone programs play a vital role in promoting equity and accessibility in communication technologies. By offering affordable smartphones and unlimited data plans, these initiatives help dismantle barriers faced by low-income populations. As our society continues to embrace the digital world, it is imperative that we advocate for and support efforts aimed at ensuring that all individuals have the tools and resources necessary to thrive. Whether through improving application processes, expanding coverage areas, or providing additional support services, the evolution of these programs will remain critical in the fight against the digital divide, fostering a more inclusive and connected future for all.
Disclaimer
1) The information above is sourced from online channels, accurate as of October 2023.
2) This article does not guarantee the chance of receiving a government-supported phone. Specific application procedures and requirements can be found directly with the providers. Real-time updates or changes may not be reflected in this document.