Managing Tardive Dyskinesia: Symptoms and Antipsychotic Drugs
Tardive Dyskinesia (TD) is a movement disorder caused by prolonged use of antipsychotic drugs. Recognizing symptoms early and managing medication can help mitigate its impact.
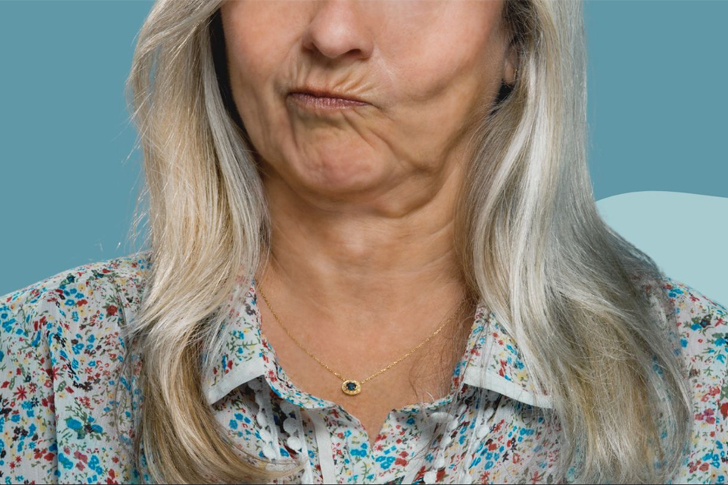

Tardive Dyskinesia (TD) is a movement disorder caused by prolonged use of antipsychotic drugs. Recognizing symptoms early and managing medication can help mitigate its impact.
Understanding Tardive Dyskinesia
Tardive Dyskinesia is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary, repetitive body movements. It often manifests in individuals who have been taking antipsychotic drugs good. These movements can include grimacing, sticking out the tongue, or jerking movements of the arms and legs.
Symptoms of Tardive Dyskinesia
Recognizing the symptoms of Tardive Dyskinesia early is crucial for effective management. The disorder can present various symptoms, including:
Facial Movements
: Involuntary movements, such as grimacing, tongue movements, and blinking.Limb Movements
: Jerking or writhing motions of the arms and legs.Body Movements
: Swaying movements of the trunk or hips.Breathing and Speech
: Irregular breathing patterns, grunting, or difficulty speaking due to muscle movements.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of Tardive Dyskinesia is prolonged exposure to antipsychotic drugs, which are used to treat psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Risk factors include:
Duration of Antipsychotic Use
: The longer the exposure, the higher the risk.Age and Gender
: Older adults and women are at higher risk.Type of Medication
: Both first-generation and second-generation antipsychotics can cause TD, though risks might vary.Genetic Factors
: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing TD.
Managing Antipsychotic Drugs
To manage the risk of developing Tardive Dyskinesia, consider the following tips regarding antipsychotic drugs:
Regular Monitoring
: Routine assessments by healthcare professionals can help detect early signs of TD.Medication Review
: Regularly review the necessity of antipsychotic medications with a healthcare provider to evaluate if the benefits outweigh the risks.Dose Management
: Use the lowest effective dose to mitigate symptoms of the underlying psychiatric condition while minimizing the risk of TD.Drug Holidays
: Consider "drug holidays" or brief periods without medication, under close medical supervision, to assess symptoms and reduce risk.Alternative Therapies
: Explore non-antipsychotic medications or adjunct therapies to manage psychiatric symptoms.
Coping with Tardive Dyskinesia Symptoms
For those already experiencing Tardive Dyskinesia symptoms, various strategies can help manage the disorder:
Lifestyle Adjustments
: Incorporate regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and sufficient rest to support overall health and well-being.Support Network
: Engage with family, friends, or support groups to share experiences and gain emotional support.Therapeutic Interventions
: Physiotherapy and occupational therapy can provide strategies to manage and reduce the impact of involuntary movements.Medical Interventions
: Consult healthcare providers about medications specifically designed to treat symptoms of TD, such as VMAT2 inhibitors.
Treatment Options
While there is no definitive cure for Tardive Dyskinesia, several treatment options can help manage symptoms:
VMAT2 Inhibitors
: Medications like valbenazine (Ingrezza) and deutetrabenazine (Austedo) have shown effectiveness in reducing TD symptoms.Switching Medications
: Transitioning to a different antipsychotic with a lower risk of causing TD, under medical supervision, may help.Botulinum Toxin Injections
: In some cases, botulinum toxin (Botox) injections can reduce muscle contractions and involuntary movements.Deep Brain Stimulation
: For severe cases, deep brain stimulation (DBS) may be considered, although it is typically regarded as a last resort.
Conclusion
Tardive Dyskinesia can significantly impact quality of life, but early recognition and proactive management can mitigate its effects. Understanding the symptoms, managing antipsychotic drug use, and exploring various treatment and coping strategies are vital steps in managing this condition. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options.
Managing Tardive Dyskinesia requires a comprehensive approach that includes regular medical supervision, lifestyle adjustments, and support from loved ones and professionals. With the right strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this condition.